Welcome to the future of food! Imagine living in a world where 3D customized meals can be printed instantly at the push of a button! 3D food printing technology has revolutionized how we approach cooking and eating.
With cutting-edge technology at our disposal, we are now capable of creating intricate edible designs using various ingredients – offering new avenues for culinary experimentation!
How does it work? It involves an amalgam of art, science and innovation.
3D food printers use computer-aided design (CAD) software to generate digital models of their desired food item and print it.
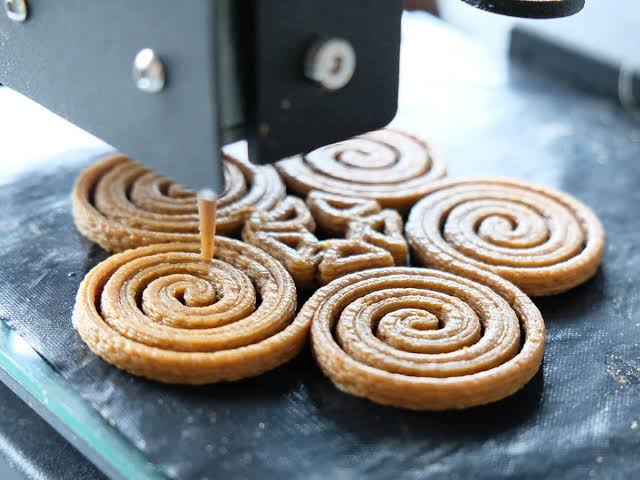
Layer by layer, the printer extrudes layers of edible materials that build the final product.
Potential advantages of this technology range from personalized nutrition to food sustainability and reduced waste.
The History of 3D Printing Food Technology
3D printing technology dates back to the 1980s when it was used primarily for rapid prototyping in manufacturing and engineering fields.
Over time, technology advanced considerably allowing complex objects made out of various materials to be printed using 3D printing technology.
Recently, researchers began exploring ways to apply 3D printing technology to food.
Initial experiments involved adapting 3D printers for use as extrusion machines for food materials like chocolate and dough.
As technology advanced, dedicated 3D food printers were manufactured, capable of handling a wider array of ingredients and producing more intricate designs.
3D food printing technology has advanced significantly over time to include printing with various edible materials – such as sugars and pastes as well as gels and powders.
The Process of 3D Printing Food
3D food printing involves several essential steps.
Start with digitalizing the food item you desire using specific software.
This digital model serves as the blueprint for the printer; then its nozzle deposits edible material layer by layer, according to its instructions from the digital model.
As layers are assembled one upon another, gradually becoming one edible object, an end-result is realized.
Preparing materials for printing requires loading them into either cartridges or syringes, depending on their printer model.
Materials can either be custom-fabricated or made available commercially to meet printing specifications.
Selecting carefully chosen for their texture, flavor and nutritional properties ensures an exquisite dining experience and delightful results.
Types of 3D food printers
There are various kinds of 3D food printers on the market today, each offering their own set of capabilities.
Some printers excel at printing intricate shapes and designs while others prioritize speed and efficiency.
From desktop printers to industrial-grade machines, these culinary-focused devices are revolutionizing the culinary landscape, giving chefs and food enthusiasts new platforms on which they can express themselves creatively.
Applications of 3D Printing Food Technology
The adoption of 3D printing food technology extends beyond the confines of the kitchen.
Various industries are harnessing its potential. In the culinary world, chefs are experimenting with 3D printed dishes, pushing the boundaries of gastronomy. Intricate sugar sculptures, personalized chocolates, and geometrically precise pastries are just a few examples of what can be achieved.
Beyond the realm of fine dining, 3D printing food technology holds the promise of addressing pressing global issues, such as food sustainability and waste reduction.
By using ingredients more efficiently and creating tailored nutrition options, we can optimize food production and minimize waste.
Additionally, the technology offers the potential for creating alternative protein sources, such as plant-based or cultured meats, reducing the environmental impact of traditional livestock farming.
Challenges and Limitations of 3D Printing Food Technology
As with any emerging technology, 3D printing food faces its share of challenges.
- One of the primary concerns is the cost associated with the technology.
Currently, 3D food printers and the specialized ingredients they require can be expensive, limiting their accessibility.
Moreover, scaling up production to meet large-scale demand poses logistical and economic challenges that need to be addressed.
- Additionally, the technology still has some limitations. The printing process can be time-consuming, making it impractical for mass production.
Some foods may require post-printing steps, such as cooking or assembly, which adds complexity and time to the overall process.
- There is also a need for further research to optimize the taste, texture, and nutritional value of 3D printed foods to match traditional cooking methods.
- Ethical considerations also arise when contemplating the future of 3D printing food. Questions regarding food safety, quality control, and the potential for replacing traditional cooking methods need to be carefully addressed.
Striking a balance between innovation and preserving culinary traditions is crucial to ensure the technology’s acceptance and success.
Future of 3D Printing Food Technology
Despite the challenges, the future of 3D printing food technology looks promising.
Ongoing research aims to refine the process, enhance the range of printable materials, and improve printing speed and efficiency.
With advancements in machine learning and artificial intelligence, we may even see printers capable of creating personalized meals based on individual dietary needs and preferences.
3D printing food technology has the potential to revolutionize the food industry and address global food challenges.
By enabling precise control over ingredients and nutrition, we can cater to diverse dietary requirements and combat malnutrition.
Additionally, the technology can empower individuals to take control of their health and make informed choices about their meals, promoting overall well-being.
Final Words on How To Print 3D Food
In conclusion, 3D printing food technology is poised to transform the way we eat and think about food.
Its origins in manufacturing and engineering have paved the way for this culinary revolution.
By combining digital design, edible materials, and precision printing, we can create delectable and visually stunning dishes.
From personalized nutrition to sustainable food production, the potential benefits are immense.
However, there are challenges to overcome, such as cost, scalability, and ethical considerations.
Addressing these issues will be crucial for the widespread adoption of 3D printing food technology.
Nonetheless, with continued research and innovation, the future holds incredible possibilities for reshaping the food industry and improving global food security.
So, get ready to savor a future where creativity and technology merge on our plates. The future of food is here, and it’s being printed in 3D.
Read Next: Mobile Phone Productivity Tips: How to use a mobile phone productively








1 comment