Are You Wondering How To Recycle Plastic Wastes Or Start Recycling Business?? Here Are Your Answers.
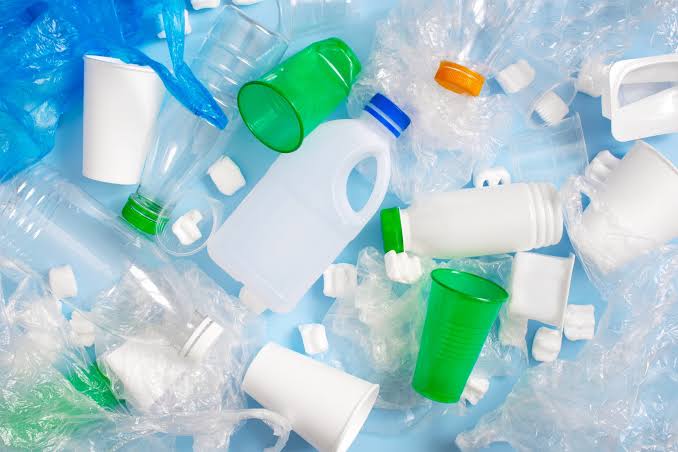
Plastic waste has emerged as one of the greatest environmental challenges of today.
Every year, millions of tons of plastic waste end up in landfills, oceans and other natural environments causing irreparable harm to ecosystems and posing serious threats to human health.
Plastic recycling stands as one of the key solutions to counter this crisis.
Recycling plastic waste provides hope for a more environmentally sustainable future.
This article presents different recycling methods, and discusses local initiatives geared at decreasing plastic waste.
Mechanical Recycling: Giving Plastic a Second Life
Mechanical recycling of plastic waste is currently the primary practiced means for recycling plastic.
Plastic recycling involves collecting, sorting and processing plastic waste to obtain raw materials that can then be used in producing new products.
Beginning with collecting plastic items and then sorting according to polymer type.
After being collected and cleaned up, plastic waste must then be shredded, melted down, and converted into pellets or flakes for recycling purposes.
These recycled materials can then be utilized to produce various goods ranging from bottles and containers, textiles and furniture.
Mechanical recycling offers several benefits.
Conserving energy and decreasing virgin plastic production reduce greenhouse gas emissions by saving both resources.
Plastic recycling helps divert plastic waste away from landfills and oceans, mitigating environmental harm caused by improper disposal.
Mechanical recycling does have some drawbacks: its success depends on having access to suitable recycling facilities, while dealing with mixed plastic waste poses numerous difficulties.
Regardless of its shortcomings, many local initiatives worldwide are using mechanical recycling to combat plastic waste.
Seattle residents can engage with the “Recycle Right” campaign to become familiar with proper recycling methods and to recycle plastic waste responsibly.
Pyrolysis: Transforming Plastic into Steel Through Heat
Pyrolysis is an innovative recycling technique which utilizes high temperatures to break down plastic waste into its component parts and recycle it back into usable forms.
Plastic can be recycled through this process by subjecting it to intense heat in an oxygen-free atmosphere, leading to its breakdown into gas, oil, and char.
These outputs can serve as valuable resources: gas can be utilized in energy production; oil may be refined into fuels for use on vehicles and aircraft, and char may serve as carbon-rich material in various applications.
Pyrolysis offers numerous advantages. It can manage mixed or contaminated plastics that might otherwise be difficult to recycle mechanically, providing another viable option for recycling plastic waste.
Furthermore, mechanical recycling only recovers a smaller percentage of materials than composting can. Furthermore, composting allows a higher proportion of plastic materials to be recovered when compared with composting methods.
Pyrolysis entails several obstacles. Notably, its operation requires significant energy inputs and emits greenhouse gasses as it proceeds.
To combat these drawbacks, it is imperative that renewable energy sources and effective emission control systems be utilized.
Local initiatives in Japan such as “Plastic to Fuel” showcase pyrolysis’s capacity to convert plastic waste to useful resources while mitigating its environmental impacts.
Challenges of Pyrolysis
However, pyrolysis also presents challenges. The process requires significant energy input and emits greenhouse gases.
To mitigate these drawbacks, it is crucial to use renewable energy sources and implement efficient emission control systems.
Local initiatives such as the “Plastic to Fuel” project in Japan exemplify the potential of pyrolysis in converting plastic waste into useful resources while minimizing environmental impact.
Chemical Recycling: Breaking Down Plastic at the Molecular Level
Chemical recycling, also known as advanced recycling, involves converting plastic waste back into its basic chemical building blocks.
This process breaks down plastic at the molecular level, enabling the creation of new plastics or other chemicals.
Different techniques, such as depolymerization and solvolysis, are employed to achieve this transformation.
Chemical recycling offers notable benefits. It can handle a wide range of plastics, including those that are difficult to recycle mechanically or through pyrolysis.
It also allows for the production of high-quality recycled plastics with properties comparable to virgin plastics. However, chemical recycling is a complex and resource-intensive process that requires significant investment and technological advancements.
Local initiatives like the “Closed-Loop Plastics Initiative” in California showcase the potential of chemical recycling in reducing plastic waste and creating a sustainable circular economy.
Biodegradation: Nature’s Way of Recycling
Biodegradation refers to the natural process by which microorganisms break down organic materials, including certain types of plastic.
Biodegradable plastics are designed to decompose under specific conditions, such as exposure to sunlight, heat, or certain enzymes.
Through biodegradation, plastic waste can be transformed into harmless substances, such as water, carbon dioxide, and biomass.
Biodegradation offers environmental benefits by reducing the accumulation of plastic waste in landfills and ecosystems.
However, it is essential to distinguish between biodegradable and conventional plastics to avoid contamination and ensure proper disposal.
Local initiatives, such as the “Compostable Packaging Program” in San Francisco, promote the use of biodegradable plastics and educate communities on proper disposal practices.
Upcycling: Transforming Waste into Valuable Creations
Upcycling is a creative recycling approach that transforms discarded plastic items into new products of higher value.
Unlike traditional recycling, which breaks down materials, upcycling repurposes them without altering their basic structure.
By using innovative design and craftsmanship, plastic waste is transformed into unique and desirable items, reducing the demand for new resources.
Upcycling offers multiple benefits. It stimulates creativity, fosters local craftsmanship, and reduces the environmental impact associated with the production and disposal of plastic items.
However, upcycling is limited by the availability of skilled artisans and the market demand for upcycled products.
Nevertheless, local initiatives like the “Plastic Fantastic” project in London demonstrate the potential of upcycling in transforming plastic waste into beautiful and functional creations.
Conclusion: Empowering Local Plastic Recycling Efforts
In conclusion, plastic recycling plays a vital role in addressing the growing problem of plastic waste.
Through mechanical recycling, pyrolysis, chemical recycling, biodegradation, and upcycling, local initiatives can actively contribute to a sustainable and circular economy.
By reducing plastic waste, conserving resources, and minimizing environmental harm, these initiatives pave the way for a cleaner and healthier planet.
To get involved in plastic recycling efforts, individuals and communities can take several actions.
Firstly, practicing responsible consumption by reducing the use of single-use plastics and opting for reusable alternatives.
Secondly, ensuring proper sorting and disposal of plastic waste to facilitate recycling processes.
Thirdly, supporting local recycling initiatives, such as collection programs or eco-brick projects, that engage the community in recycling efforts.
Finally, advocating for sustainable policies and regulations that promote recycling and incentivize innovation in plastic waste management.
Together, by embracing plastic recycling and taking collective action, we can make a significant impact in mitigating the plastic waste crisis and creating a more sustainable future for generations to come.